TV receiver
The receiving
antenna intercepts the radiated picture and sound carrier signals and feeds them
to the RF tuner . The receiver is of the heterodyne type and employs two or three
stages of intermediate frequency (IF) amplification. The output from the last
IF stage is demodulated to recover the video signal. This signal that carries
the picture information is
amplified and coupled to the picture tube
which converts the electrical signal back into picture elements of the same
degree of black and white.
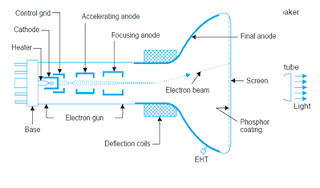
The glass envelope
contains an electron gun structure that produces a beam of electrons aimed at
the fluorescent screen. When the Electron beam strikes the screen, light is
emitted. The beam is deflected by a pair of deflecting coils mounted on the
neck of the picture tube in the same way and rate as the beam scans the target in
the camera tube. The amplitudes
of the currents in the horizontal and vertical deflecting coils are so adjusted
that the entire screen, called raster, gets illuminated because of the fast rate
of scanning.
The
video signal is fed to the grid or cathode of the picture tube. When the
varying
signal voltage makes the control grid less negative,
the beam current is increased, making the
spot of light on the screen brighter. More
negative grid voltage reduces the brightness. If the
grid voltages is negative enough to cut-off
the electron beam current at the picture tube there
will be no light. This state corresponds to
black. Thus the video signal illuminates the fluorescent screen from white to
black through various shades of grey depending on its amplitude at any instant.
This corresponds to the brightness changes encountered by the electron beam of
the camera tube while scanning the picture details element by element. The rate
at which the spot of light moves is so fast that the eye is unable to follow it
and so a complete picture is seen because of the storage capability of the
human eye.
Sound reception
The
path of the sound signal is common with the picture signal from antenna to the
video detector section of the receiver. Here the two signals are separated and
fed to their respective channels. The frequency modulated audio signal is
demodulated after at least one stage of amplification. The audio output from
the FM detector is given due amplification before feeding it to the
loudspeaker.
Synchronization
It is
essential that the same coordinates be scanned at any instant both at the camera
tube target plate and at the raster of the picture tube, otherwise, the picture
details would split and get distorted. To ensure perfect synchronization
between the scene being televised and the picture produced on the raster,
synchronizing pulses are transmitted during the retrace, i.e., fly-back
intervals of horizontal and vertical motions of the camera scanning beam. Thus,
in addition to carrying picture detail, the radiated signal at the transmitter
also contains
synchronizing pulses. These pulses which are
distinct for horizontal and vertical motion control, are processed at the
receiver and fed to the picture tube sweep circuitry thus ensuring that the receiver
picture tube beam is in step with the transmitter camera tube beam.
Receiver controls
The
front view of a typical monochrome TV receiver, having various controls is
shown in Fig. The channel selector switch is used for selecting the desired
channel. The fine tuning control is provided for obtaining best picture details
in the selected channel. The hold control is used to get a steady picture in
case it rolls up or down. The brightness control varies the beam intensity of
the picture tube and is set for optimum average brightness of the picture. The
contrast control is actually the gain control of the video amplifier. This can
be varied to obtain the desired contrast between the white and black contents
of the reproduced picture. The volume and tone controls form part of the audio
amplifier in the sound section, and are used for setting the volume and tonal
quality of the sound output from the loudspeaker
Picture and Sound reception in TV
 Reviewed by Sikha
on
December 04, 2015
Rating:
Reviewed by Sikha
on
December 04, 2015
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sikha
on
December 04, 2015
Rating:
Reviewed by Sikha
on
December 04, 2015
Rating:




No comments:
Post a Comment