Cyclotron
Cyclotron is a machine to accelerate charged
particles or ions to high energies. It was invented by E.O Lawrence and M.S
Livingston.
- Cyclotron uses both electric
and magnetic fields in combination to increase the energy of charged
particles.
- The electric and magnetic
fields are perpendicular to each other ( and called as crossed fields)
- Principle:- the frequency of revolution of the charged particle in a magnetic field is independent of its energy.
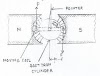
Working:
o
The
particles move most of the time inside two semi circular disc –like metal
containers, D1 and D2
, which are called ‘dees’ ( as they look
like the letter ‘D’)
o
Inside
the metal boxes, the particle is shielded and is not acted on by the electric
field.
o
The
magnetic field acts on the particle and makes it go round in a circular path
inside the dee.
o
Every
time the particle moves from one dee to another, it is acted upon by the
electric field.
o
The
sign of the electric field is changed alternately in tune with the circular
motion of the particle.
o
Thus,
the particle is always accelerated by the electric field
o
Each
time, the acceleration increases the energy of the particle.
o
As
energy increases, the radius of the circular path also increases. So, the path
is a spiral one.
o
The
whole assembly is evacuated to minimize collisions between the ions and the air
molecules.
o
A
high frequency a.c voltage is applied to the dees.
In the fig, positive ions or positively charged
particles (protons) are released at the centre P. They move in a semi-circular
path in one of the dees and arrive in the gap between the dees in a time
interval T/2.
T- period of revolution.
T=1/fC = 2πm/qB
Or , fC = qB/2 πm
fC – Cyclotron frequency
fa – frequency of applied voltage
At resonance, fC = fa
- The phase of the supply is
adjusted so that when the positive ions arrive at the edge of D1, the dee D2 is at a lower
potential and the ions are accelerated across the gap.
- Inside the dees, the particles
travel in a region free of the electric field.
- The increase in their K.E = qV
each time they cross from one dee to another.
- (V= the voltage across the dees
at that time)
- Thus, radius of the path
increases each time they cross the dees.
- The ions are repeatedly
accelerated across the dees until they have the required energy to have a
radius approximately equal to that of the dees.
- They are then deflected by a
magnetic field and leave the system via an exit slip.
From
Applications
- Used to bombard nuclei with
energetic particles to accelerate nuclei and study the resulting nuclear
reactions
- Used to implant ions in to
solids and modify their properties. Or to synthesize new materials.
- Used in hospitals to produce
radio active substances that can be used in diagnosis and treatment.
Cyclotron
 Reviewed by Sikha
on
August 13, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by Sikha
on
August 13, 2017
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sikha
on
August 13, 2017
Rating:
Reviewed by Sikha
on
August 13, 2017
Rating:









No comments:
Post a Comment