Electric current
Electric
current is the rate of flow of electric charges. Electrons are negatively
charged particles and their flow in conductors results in electric current.
By definition, current,
If Q is the amount of charge flowing
through a conductor in T seconds, then current I is given by the expression,
The unit of charge is Coulomb. 1 Coulomb =
6.24×1018 electrons. The unit of current is Ampere(A). 1 Ampere= 1
Coulomb/sec.
Electromotive
force(e.m.f)
Energy
is required for the movement of charge from one point to another. Inorder to
move electrons along a conductor, some amount of work is required. The work
required is supplied by an electromotive force(e.m.f) provided by a battery or
a similar device.
Potential
difference
Potential
difference is the difference between the voltages at two ends of a conductor.
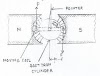
A
current carrying element is shown in the fig above. The voltage across the
element, Vab is given by,
Where work done (W) is measured in Joules
and the charge (Q) in Coulombs.
The positive (+) and negative (-)
signs shown in fig. define the polarity of the voltage Vab. With
this definition, Vab represents the voltage at point ‘a’ relative to
point ‘b’.
Introductory concepts
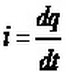 Reviewed by Sikha
on
December 29, 2012
Rating:
Reviewed by Sikha
on
December 29, 2012
Rating:
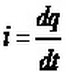 Reviewed by Sikha
on
December 29, 2012
Rating:
Reviewed by Sikha
on
December 29, 2012
Rating:


.jpg)






No comments:
Post a Comment