An
electrical machine is an electromechanical energy conversion device. The device
which converts electrical energy in to mechanical energy is called a motor. The
device which converts mechanical energy in to electrical energy is called a
generator.
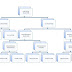
Classification
of electrical machines
D.C generator
D.C
generator is a machine which converts mechanical energy in to electrical
energy. Direct –current generators are used to supply power for radio equipment, for battery
charging
for
electrolytic cells etc. a disadvantage common to all d.c machines is the
complexity of design, mainly due to the usage of brushgear. This brush gear can
also cause sparking.
A d.c machine consists essentially a
stationary part, called the field structure and a rotating part called, the
armature.
Principle of operation:
D.C generator is based on the
principle that whenever magnetic flux is cut by a moving conductor, an e.m.f is
induced in the conductor as per Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction.
The e.m.f so induced is an alternating e.m.f. it is made unidirectional with
the help of commutator and brushes. This e.m.f causes the flow of current in the
external circuit if the circuit is closed.
The direction of induced e.m.f is
given by Fleming’s right hand rule. Stretch out the right hand with first
finger, middle finger and thumb mutually perpendicular to each other. If the
first finger points in the direction of flux, and thumb in the direction of
motion of the conductor, then the middle finger will point in the direction of
the induced e.m.f..
Constructional details:-
The main parts of a d.c machine (a
generator or a motor) are described below.
1)
Yoke:-
It is the outermost cylindrical part of
the machine. The yoke is made of cast iron or cast steel or forged steel. The
yoke acts as the supporting frame for the machine and also completes the path
of the main magnetic flux. In small d.c machines, yoke is made up of cast iron.
In large d.c generators, the yoke is made of cast steel from the consideration
of better magnetic properties.
2)
Poles:-
The
pole consists of pole core and pole shoe. The field coil is wound on the pole
core. The poles are made of cast steel or forged steel. In some machines, poles
are made from laminated sheet steel. The main functios of the pole shoe are (a)
it supports the field coil. (b) it spreads out the magnetic flux in the air
gap. (since pole shoe is of large cross section, it reduces the reluctance of
the magnetic path.
3)
Field
coils:-
The
field coils are wound on pole cores. They are connected in series and the
connections are arranged so that due to the flow of current in these coils
alternate N and S poles are made. The field coils are made from enameled copper
wire.
4)
Armature:-
The
armature is that part of the d.c machine where an e.m.f is induced as it
rotates relative to the main field. The armature consists of the toothed core,
a winding dropped in the core slots, and a commutator mouted on the armature
shaft. The armature core is composed of silicon- steel laminations. The
armature winding consists of sections or coils.
5)
Commutator:-
The commutator, which is a typical component of d.c
machines, is a hollow cylinder. The commutator is made up of wedge shaped
segments of hogh conductivity hard drawn or copper forged copper. The segments
are insulated from each other by thin layer of mica. The function of the
commutator is to convert the e.m.f induced in the armature conductors in to
unidirectional voltage across the load impedance.
6)
Brushes:-
The
function of the brush is to collect current from the rotating commutator and
deliver it to the external load impedance. The brushes are made of carbon. The
brushes are mounted in a box type of brush holder and are held on the
commutator by a spring.
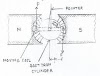
Simple d.c generator
The fig. gives the basic structure. When a coil is
rotated in a uniform magnetic field, an alternating emf is generated across the
terminals 1 and 2 of the coil. If a unidirectional current is desired in the
external circuit, the two ends of the coil ABCD are connected to the two
segments C1 and C2 which are insulated from each other.
When C1 is positive, the brush B1 makes contact with it.
But for the other half rotation, of the coil, the segment C2 becomes
positive and now this makes contact with the brush B2. Thus, we see
that the brush remains positive all the time, and hence a unidirectional
current results in the external circuit as shown below.
The current in the external circuit is
unidirectional. But its strength varies considerably. It raises and falls
between zero and maximum for each half rotation of the coil. This defect of
having large variations in the unidirectional e.m.f (or current) can be
overcome by having more coils on the rotor.
Types of D.C
generator:-
D.C
generators are generally classified according to the method used for field
excitation. Thus, they can be classified as
1. Separately
excited generator
2. Self
excited generator
D.C Machines
 Reviewed by Sikha
on
July 03, 2013
Rating:
Reviewed by Sikha
on
July 03, 2013
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sikha
on
July 03, 2013
Rating:
Reviewed by Sikha
on
July 03, 2013
Rating:








No comments:
Post a Comment